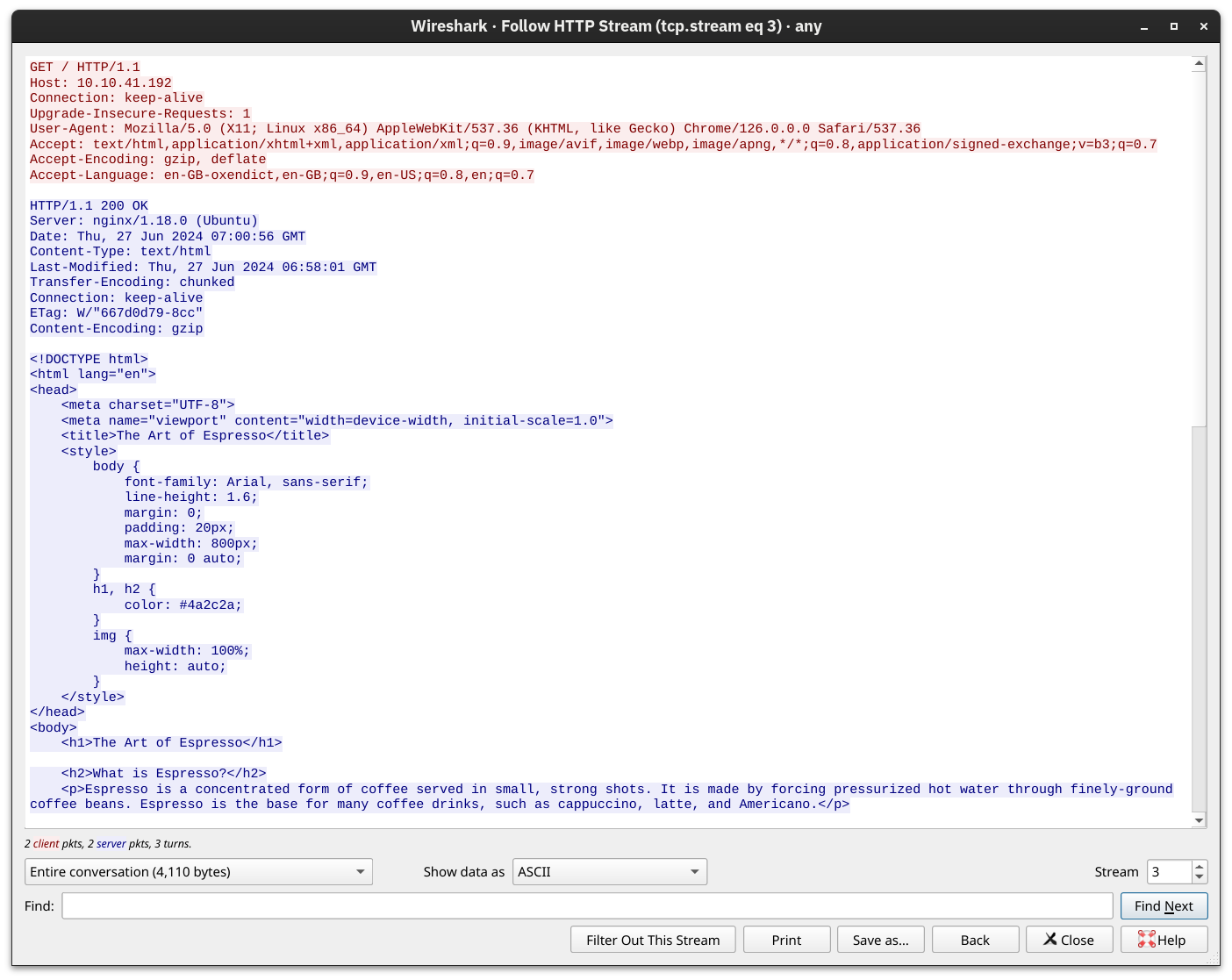
OSI Model
Mnemonic: Please Do Not Throw Salami Pizza Away (Layer 7 → 1)
| Layer | Name | Function | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | Application | User apps (HTTP, FTP, email) | HTTP, DNS, SMTP, POP3 |
| 6 | Presentation | Data translation (encryption/compression) | JPEG, PNG, MPEG, Unicode |
| 5 | Session | Manages connections (start/stop sessions) | NFS, RPC |
| 4 | Transport | Reliable data delivery (TCP/UDP) | TCP (safe), UDP (fast) |
| 3 | Network | Logical addressing & routing | IP, ICMP, IPSec |
| 2 | Data Link | MAC addressing & local delivery | Ethernet (802.3), WiFi (802.11) |
| 1 | Physical | Raw bit transmission (cables, signals) | Fiber, Copper, Radio |
Encapsulation
How data travels down OSI layers:
- Application: User data (e.g., email) → Formatted as HTTP/FTP.
- Transport: Adds TCP/UDP header → Creates segment/datagram.
- Network: Adds IP header → Creates packet.
- Data Link: Adds MAC header/trailer → Creates frame.
- Physical: Converts to bits → Sent via cable/WiFi.
Core Protocols
1. DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
- Purpose: Auto-assigns IP, subnet, DNS, gateway.
- Port: UDP 67 (server), 68 (client).
- DORA Process:
- Discover: Client broadcasts “Need IP” (
0.0.0.0→255.255.255.255). - Offer: Server responds with IP offer.
- Request: Client accepts.
- Ack: Server confirms.
- Discover: Client broadcasts “Need IP” (
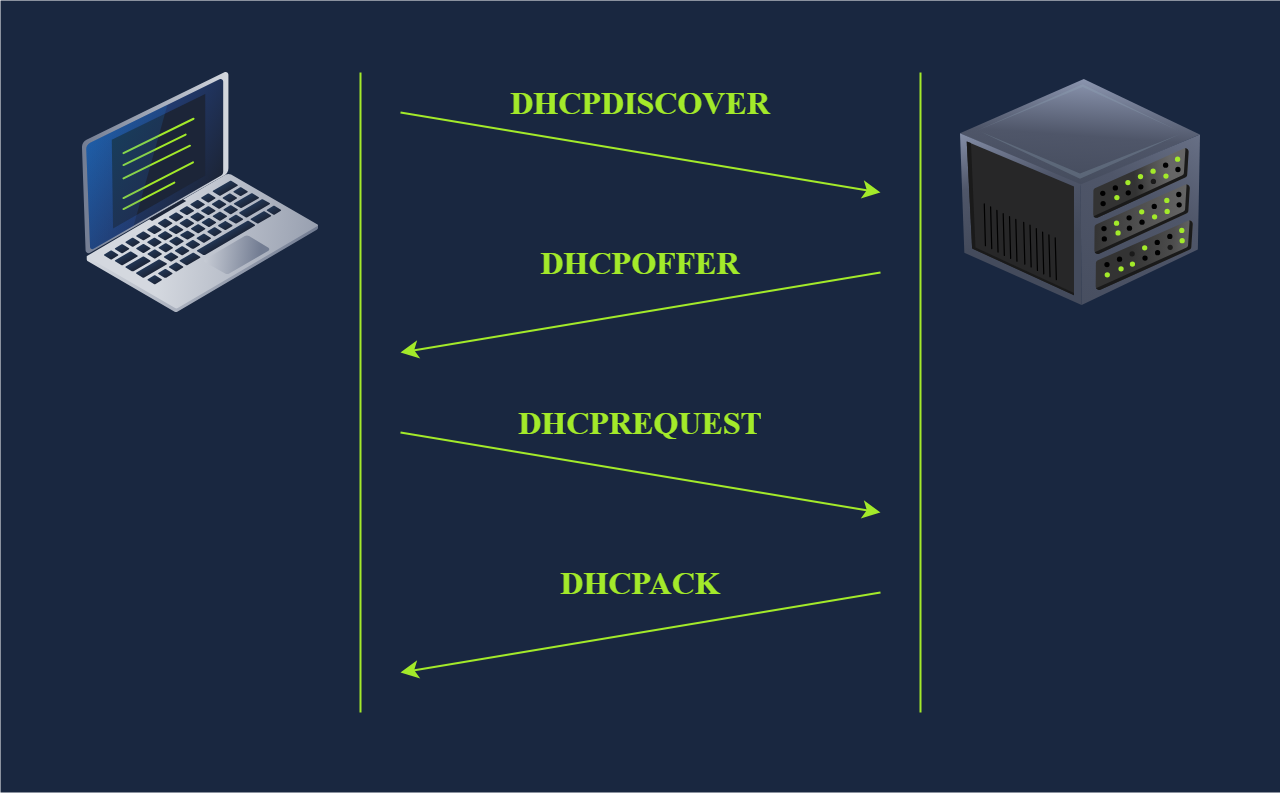
2. ARP (Address Resolution Protocol)
- Purpose: Maps IP → MAC address.
- Process:
- Request: “Who has
192.168.1.1?” (Broadcast:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff). - Reply: “
192.168.1.1is at44:df:65:d8:fe:6c”.
- Request: “Who has
3. ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol)
- Purpose: Network troubleshooting (
ping,traceroute). - Commands:
ping <IP> -c 4 # Stop after 4 packets traceroute google.com # Path to destination
4. DNS (Domain Name System)
- Purpose: Resolves
example.com→93.184.215.14. - Record Types:
- A: IPv4 address.
- AAAA: IPv6 address.
- CNAME: Alias (
www.example.com→example.com). - MX: Mail server.
- Tools:
nslookup example.com # Query DNS whois example.com # Domain ownership
5. HTTP/HTTPS
| Feature | HTTP (Port 80) | HTTPS (Port 443) |
|---|---|---|
| Security | Plaintext | Encrypted (TLS) |
| Methods | GET, POST, PUT, DELETE | Same + TLS |
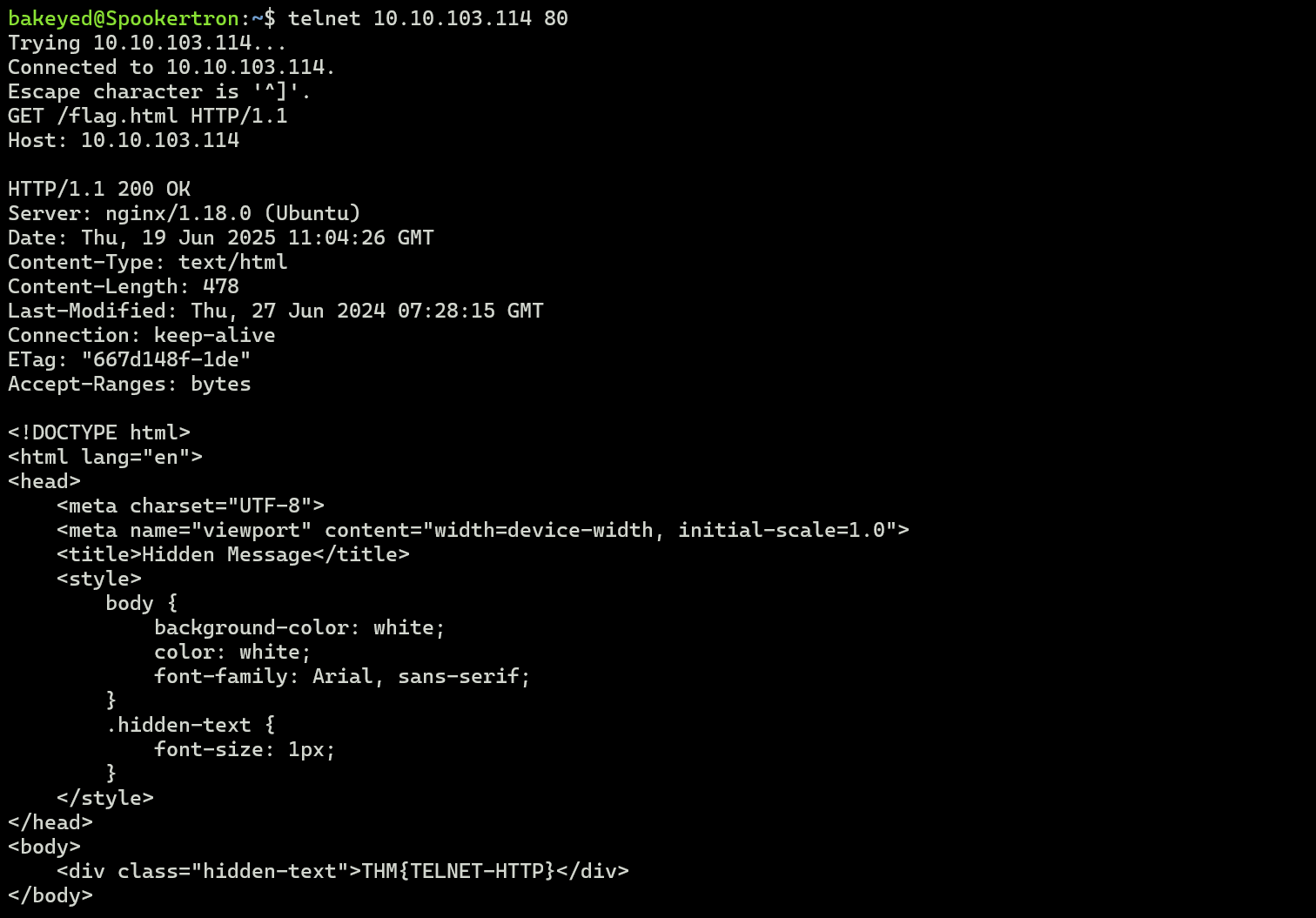
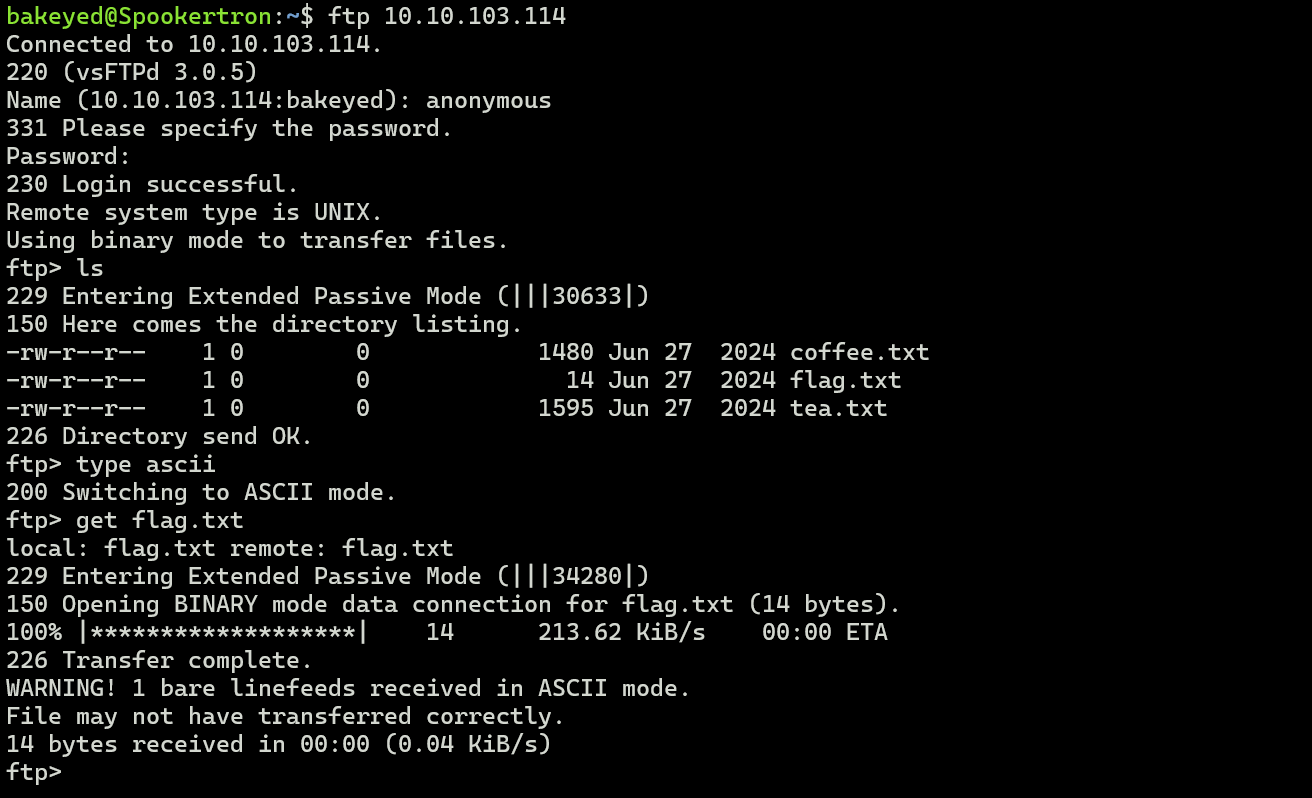
6. FTP (File Transfer Protocol)
- Port: 21 (control), 20 (data).
- Commands:
USER,PASS: Login.RETR: Download.STOR: Upload.
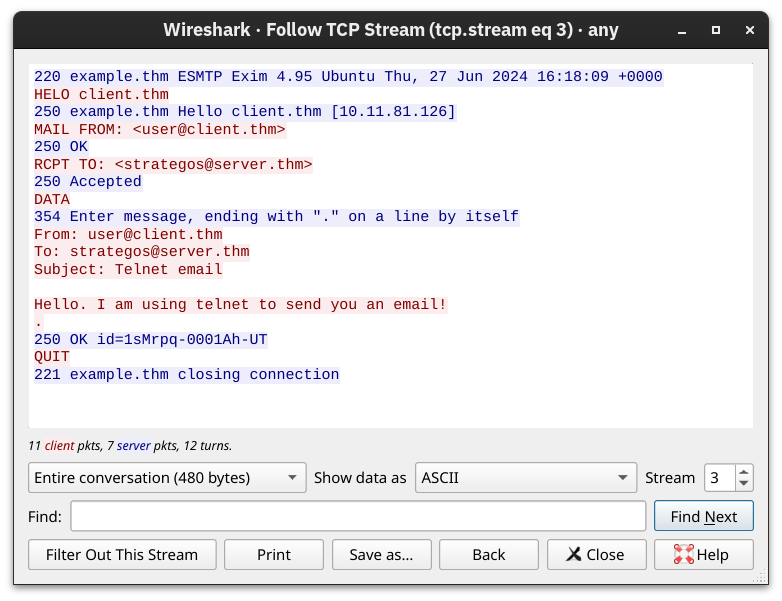
7. SMTP (Email Sending)
- Port: 25 (unencrypted), 465/587 (encrypted).
- Commands:
HELO: Start session.MAIL FROM: Sender.RCPT TO: Recipient.DATA: Email content.
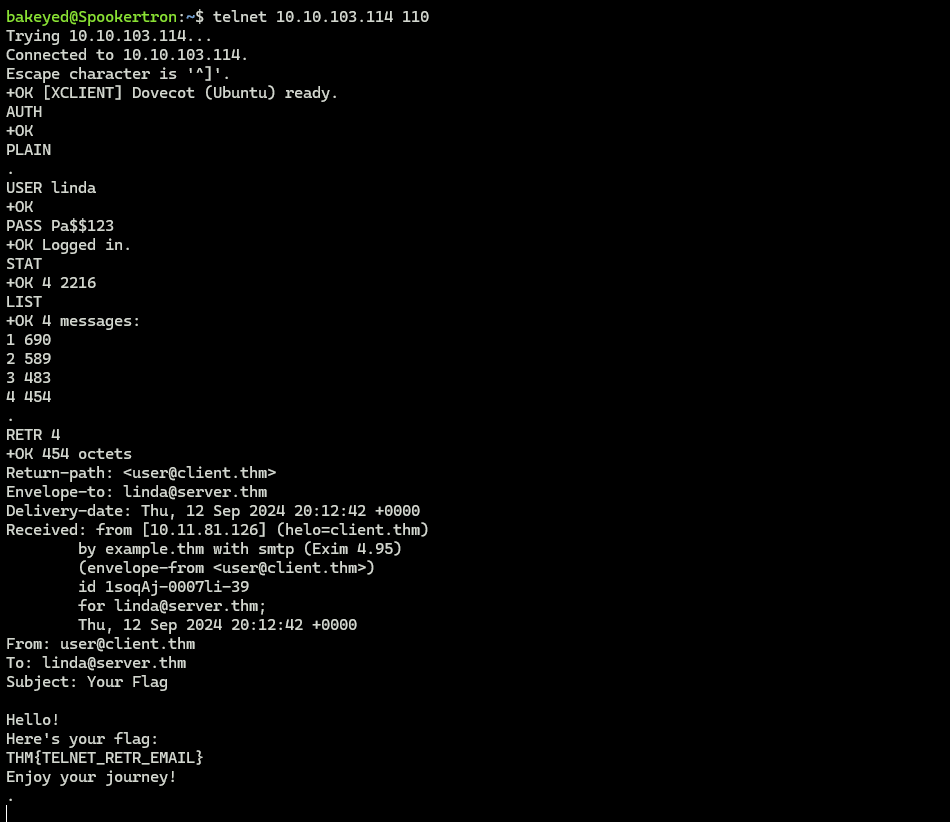
8. POP3/IMAP (Email Retrieval)
| POP3 (Port 110) | IMAP (Port 143) |
|---|---|
| Downloads & deletes | Syncs across devices |
Secure Protocols (TLS/SSL)
- HTTPS: HTTP + TLS (Port 443).
- SSH: Encrypted remote access (Port 22).
- SMTPS: SMTP + TLS (Port 465/587).